MapOutputTracker用于跟踪map任务的输出状态,此状态便于reduce任务定位map输出结果所在的节点地址,进而获取中间输出结果
MapStatus
保存ShuffleMapTask返回给调度器的结果,该特质有以下未实现的方法
location:BlockManagerId,task运行的位置即结果所在位置getSizeForBlock(): 返回shuffle中间数据中,指定reduce id在此map任务中所依赖的数据大小,单位为字节
有实现类CompressedMapStatus, HighlyCompressedMapStatus
ShuffleStatus
帮助MapOutputTrackerMaster记录单个ShuffleMapStage的状态
有以下成员属性
numPartitionsmapStatuses:Array[MapStatus](numPartitions)。如果未计算完则对应partition中为nullcachedSerializedStatuses: 缓存shuffleId与序列化MapStatus的映射关系cachedSerializedBroadcast: 与cachedSerializedStatuses一致的广播变量,当序列化MapStatuses太大而无法在单个RPC中发送时应通过广播变量获取,此变量保存广播变量的引用防止被GC_numAvailableOutputs: 跟踪已完成的partition总数
有以下成员方法
addMapOutput(): 向mapStatuses注册一个map输出,并调用invalidateSerializedMapOutputStatusCache()清除缓存removeMapOutput(): 向mapStatuses移除一个map输出,并调用invalidateSerializedMapOutputStatusCache()清除缓存removeOutputsByFilter(): 移除在mapStatuses中满足过滤器的map输出,并调用invalidateSerializedMapOutputStatusCache()清除缓存removeOutputsOnHost(),removeOutputsOnExecutor(): 清除指定Host或者Executor上的map输出invalidateSerializedMapOutputStatusCache(): 清除cachedSerializedBroadcast广播变量def invalidateSerializedMapOutputStatusCache(): Unit = synchronized { if (cachedSerializedBroadcast != null) { Utils.tryLogNonFatalError { // Use `blocking = false` so that this operation doesn't hang while trying to send cleanup // RPCs to dead executors. cachedSerializedBroadcast.destroy(blocking = false) } cachedSerializedBroadcast = null } cachedSerializedMapStatus = null }findMissingPartitions(): 返回未计算完的partition id序列serializedMapStatus(): 优先返回已经缓存cachedSerializedStatuses,如果缓存为空则调用MapOutputTracker.serializeMapStatuses()对mapStatuses序列化后返回并放入cachedSerializedStatuses,如果长度大于minBroadcastSize还会将序列化的数据放入广播变量cachedSerializedBroadcast
MapOutputTracker
抽象类,跟踪stage的map输出的位置,有两个实现类MapOutputTrackerMaster和MapOutputTrackerWorker
下面是一些重要成员属性
trackerEndpoint: 持有Driver上MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint的RpcEndpointRefmapStatuses:Map[Int, Array[MapStatus]]维护shuffle id与其各个map task的输出状态。由于各个MapOutputTrackerWorker会向MapOutputTrackerMaster不断汇报map任务的状态信息,因此MapOutputTrackerMaster的mapStatuses中维护的信息是最新最全的。MapOutputTrackerWorker的mapStatuses对于本节点Executor运行的map任务状态是及时更新的,而对于其他节点上的map任务状态则更像一个缓存,在mapStatuses不能命中时会向Driver上的MapOutputTrackerMaster获取最新的任务状态信息fetching:HashSet[Int]shuffle id集合,用来记录当前Executor正在从哪些map输出的位置拉取数据
下面是一些实现的方法
askTracker(): 向MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint发送消息,并期望在超时时间之内得到回复sendTracker(): 向MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint发送消息,并期望在超时时间之内获得的返回值为true
MapOutputTrackerMaster
在Spark中的变量名mapOutputTracker一般指的是MapOutputTrackerMaster。MapOutputTrackerMaster负责整理和维护由MapOutputTrackerWorker发送的所有的map任务的输出跟踪信息,只存在于Driver上。
下面是一些重要的成员属性
SHUFFLE_PREF_MAP_THRESHOLD,SHUFFLE_PREF_REDUCE_THRESHOLD: 当map或者reduce task的数量超过这个限制将不会分配偏好位置,因为这样做更昂贵。默认为1000REDUCER_PREF_LOCS_FRACTION: 当某个map task输出占比超过这个比例后,增大这个比例以实现本地读取。默认为0.2minSizeForBroadcast: 用于广播的最小大小,使用广播变量将map输出信息传递给Executor。通过spark.shuffle.mapOutput.minSizeForBroadcast属性配置,默认为512KB。minSizeForBroadcast必须小于maxRpcMessageSizeshuffleLocalityEnabled: 是否为reduce任务计算本地性偏好。通过spark.shuffle.reduceLocality.enabled属性进行配置,默认为trueshuffleStatuses:ConcurrentHashMap[Int, ShuffleStatus]维护了shuffle id和ShuffleStatus的映射关系maxRpcMessageSize: 最大的Rpc消息的大小。通过spark.rpc.message.maxSize属性进行配置,默认为128MB。minSizeForBroadcast必须小于maxRpcMessageSizemapOutputRequests:LinkedBlockingQueue[GetMapOutputMessage]缓存获取map输出状态的请求消息threadpool: 用于获取map输出的固定大小的线程池。此线程池提交的线程都以后台线程运行,且线程名以map-output-dispatcher为前缀,线程池大小可以使用spark.shuffle.mapOutput.dispatcher.numThreads属性配置,默认大小为8- 在
MessageLoop中,循环取出阻塞队列mapOutputRequests中的GetMapOutputMessage直至遇到PoisonPill - 根据消息中的shuffle id在
shuffleStatuses取出shuffleStatus,调用serializedMapStatus()对shuffleStatus中的mapStatuses进行序列化并返回
private val threadpool: ThreadPoolExecutor = { val numThreads = conf.getInt("spark.shuffle.mapOutput.dispatcher.numThreads", 8) val pool = ThreadUtils.newDaemonFixedThreadPool(numThreads, "map-output-dispatcher") for (i <- 0 until numThreads) { pool.execute(new MessageLoop) } pool } private class MessageLoop extends Runnable { override def run(): Unit = { try { while (true) { try { val data = mapOutputRequests.take() if (data == PoisonPill) { // Put PoisonPill back so that other MessageLoops can see it. mapOutputRequests.offer(PoisonPill) return } val context = data.context val shuffleId = data.shuffleId val hostPort = context.senderAddress.hostPort logDebug("Handling request to send map output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId + " to " + hostPort) val shuffleStatus = shuffleStatuses.get(shuffleId).head context.reply( shuffleStatus.serializedMapStatus(broadcastManager, isLocal, minSizeForBroadcast)) } catch { case NonFatal(e) => logError(e.getMessage, e) } } } catch { case ie: InterruptedException => // exit } } }- 在
PoisonPill: 毒药GetMapOutputMessage
有以下重要的成员方法
post(): 向阻塞队列mapOutputRequests中添加消息交由MessageLoop线程去处理,主要由MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint接收消息并调用// MapOutputTrackerMaster def post(message: GetMapOutputMessage): Unit = { mapOutputRequests.offer(message) } /** RpcEndpoint class for MapOutputTrackerMaster */ private[spark] class MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint( override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv, tracker: MapOutputTrackerMaster, conf: SparkConf) extends RpcEndpoint with Logging { logDebug("init") // force eager creation of logger override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = { case GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId: Int) => val hostPort = context.senderAddress.hostPort logInfo("Asked to send map output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId + " to " + hostPort) val mapOutputStatuses = tracker.post(new GetMapOutputMessage(shuffleId, context)) case StopMapOutputTracker => logInfo("MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint stopped!") context.reply(true) stop() } }registerShuffle(): 注册shuffle iddef registerShuffle(shuffleId: Int, numMaps: Int) { if (shuffleStatuses.put(shuffleId, new ShuffleStatus(numMaps)).isDefined) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Shuffle ID " + shuffleId + " registered twice") } }registerMapOutput(): 在shuffle中注册MapStatusdef registerMapOutput(shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int, status: MapStatus) { shuffleStatuses(shuffleId).addMapOutput(mapId, status) }unregisterMapOutput(),unregisterAllMapOutput(),unregisterAllMapOutput(),unregisterShuffle(),removeOutputsOnHost(),removeOutputsOnExecutor(): 注销对应的信息getMapSizesByExecutorId(): 获取某个shuffle中,reducer partition所要获取的map输出的对应的block序列(一个reducer需要读取多个map端的block)getPreferredLocationsForShuffle(): 获取某个shuffle中,reducer partition所要获取的map输出数据占比超过REDUCER_PREF_LOCS_FRACTION的Executor列表,这将作为此reducer partition的偏好位置
MapOutputTrackerWorker
Executor端维护map输出信息
有以下成员属性
mapStatuses:ConcurrentHashMap[Int, Array[MapStatus]]。维护本地map输出状态fetching:HashSet[Int]。缓存已经请求过的shuffle id
下面是重要的成员方法
getStatus(): 根据shuffleId获取map状态信息数组- 首先尝试返回本地缓存
mapStatuses中对应的map状态信息 - 如果没有则判断
fetching中有没有该shuffle id - 如果有,说明有其他线程正在请求map状态信息,此时等待fetching的对象锁并再次从
mapStatuses本地缓存中获取 - 如果没有,直接调用
askTracker()方法向MapOutputTrackerWorker发送GetMapOutputStatuses请求消息获取对应shuffle的map状态信息。放入本地缓存,从fetching中移除并唤醒等待在此对象锁的线程
private def getStatuses(shuffleId: Int): Array[MapStatus] = { val statuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull if (statuses == null) { logInfo("Don't have map outputs for shuffle " + shuffleId + ", fetching them") val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis var fetchedStatuses: Array[MapStatus] = null fetching.synchronized { // Someone else is fetching it; wait for them to be done while (fetching.contains(shuffleId)) { try { fetching.wait() } catch { case e: InterruptedException => } } // Either while we waited the fetch happened successfully, or // someone fetched it in between the get and the fetching.synchronized. fetchedStatuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull if (fetchedStatuses == null) { // We have to do the fetch, get others to wait for us. fetching += shuffleId } } if (fetchedStatuses == null) { // We won the race to fetch the statuses; do so logInfo("Doing the fetch; tracker endpoint = " + trackerEndpoint) // This try-finally prevents hangs due to timeouts: try { val fetchedBytes = askTracker[Array[Byte]](GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId)) fetchedStatuses = MapOutputTracker.deserializeMapStatuses(fetchedBytes) logInfo("Got the output locations") mapStatuses.put(shuffleId, fetchedStatuses) } finally { fetching.synchronized { fetching -= shuffleId fetching.notifyAll() } } } logDebug(s"Fetching map output statuses for shuffle $shuffleId took " + s"${System.currentTimeMillis - startTime} ms") if (fetchedStatuses != null) { fetchedStatuses } else { logError("Missing all output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId) throw new MetadataFetchFailedException( shuffleId, -1, "Missing all output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId) } } else { statuses } }- 首先尝试返回本地缓存
getMapSizesByExecutorId(): 调用了getStatus(),效果与MapOutputTrackerWorker.getMapSizesByExecutorId()类似
总结
如果所示,这是MapOutTrackerMaster应答获取shuffle信息的流程
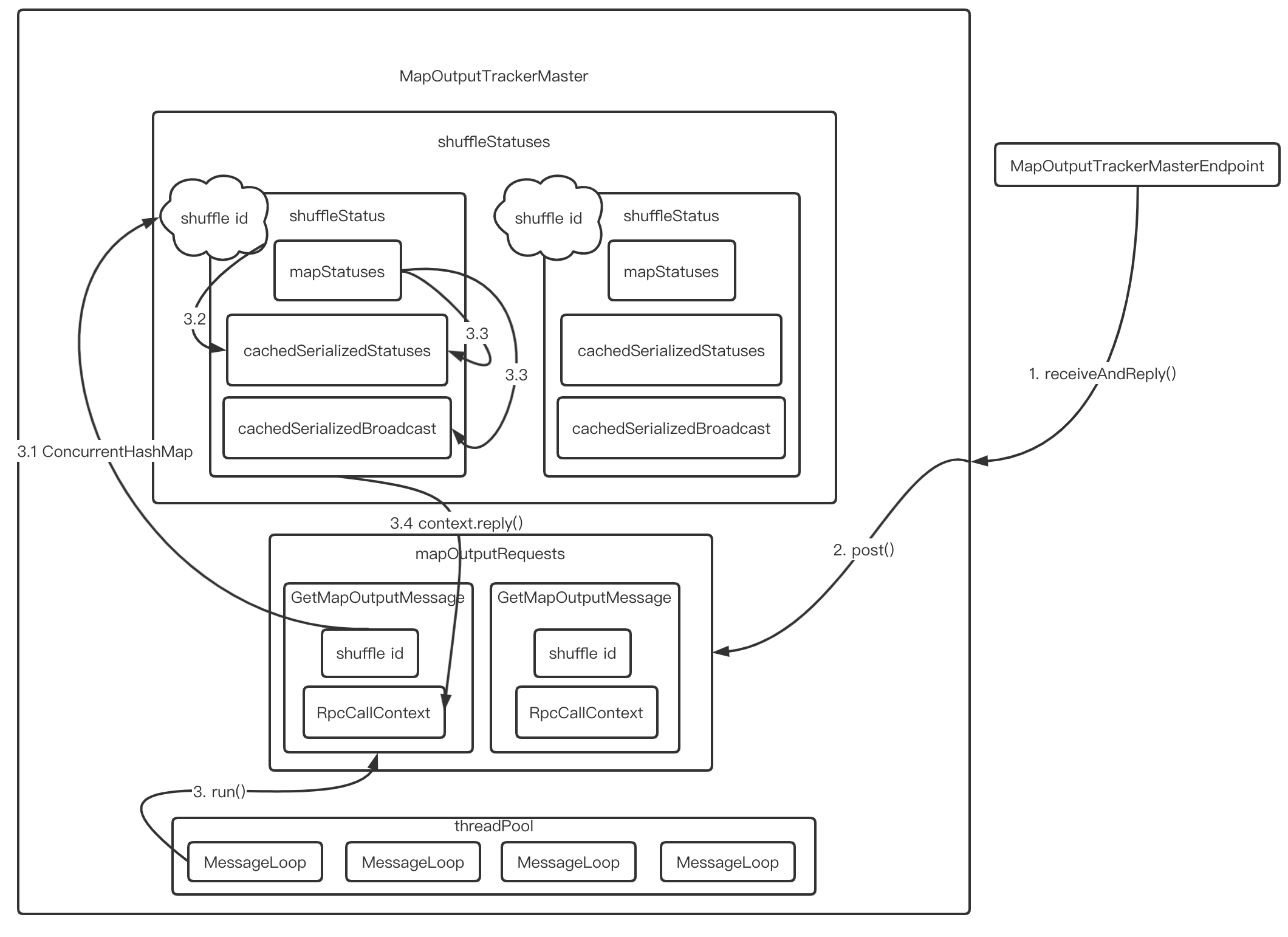
MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint接收到MapOutputTrackerWorker.getStatuses()发送的GetMapOutputStatuses请求- 于是调用
MapOutputTrackerMaster.post()将请求消息放入mapOutputRequests中 MapOutputTrackerMaster中的线程池的MessageLoop线程会循环从mapOutputRequests阻塞队列中取出消息- 由消息中的shuffle id,在
shuffleStatuses中找到对应的ShuffleStatus并调用ShuffleStatus.serializedMapStatus()方法获取序列化后的MapStatuses - 首先从缓存的
cachedSerializedStatuses返回 - 如果没有则将原始的
MapStatuses序列化后放入缓存并返回 - 调用
context.reply()回调方法将序列化后的数据恢复消息请求者
- 由消息中的shuffle id,在
如图所示,这是在MapOutputTrackerMaster中的shuffle注册流程
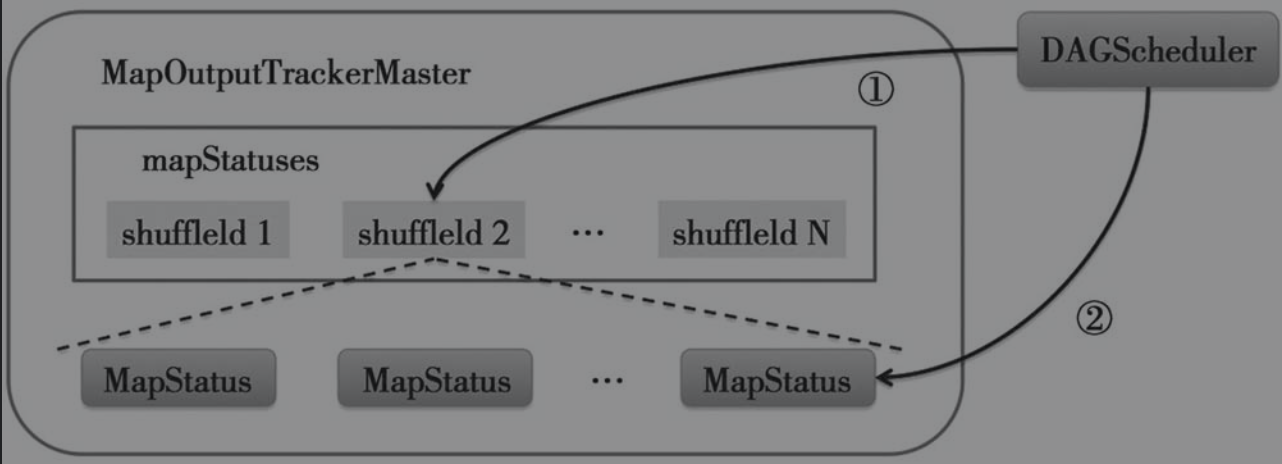
DAGScheduler在创建了ShuffleMapStage后,调用MapOutputTrackerMaster.registerShuffle()方法向shuffleStatuses缓存注册shuffle idDAGScheduler处理ShuffleMapTask的执行结果时,如果发现ShuffleMapTask所属的ShuffleMapStage中每一个partition的ShuffleMapTask都执行成功了,那么将调用MapOutputTrackerMaster.registerMapOutputs()方法,将ShuffleMapStage中每一个ShuffleMapTask的MapStatus保存到对应的ShuffleStatuse中
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://wzx140.github.io//2020/09/22/schedule-mapTrack/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)