介绍Spark中的调度池包括TaskSetManager
调度算法
调度池对TaskSet的调度取决于调度算法。特质SchedulingAlgorithm定义了调度算法的规范,其两个子类FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm先进先出调度算法和FairSchedulingAlgorithm公平调度算法
FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm
实现的comparator()方法用于比较两个实现Schedulable特质的对象,优先调度优先级小的,如果相同则优先调度stage id小的
private[spark] class FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm extends SchedulingAlgorithm {
override def comparator(s1: Schedulable, s2: Schedulable): Boolean = {
val priority1 = s1.priority
val priority2 = s2.priority
var res = math.signum(priority1 - priority2)
if (res == 0) {
val stageId1 = s1.stageId
val stageId2 = s2.stageId
res = math.signum(stageId1 - stageId2)
}
res < 0
}
}
FairSchedulingAlgorithm
- 如果s1和s2中有且只有一个的运行任务数量比其最小分享量
minShare小,说明该调度对象运行的任务太小不公平,优先调度该对象 - 如果都小于自身的最小分享量,则计算当前运行任务数量占其最小分享量。优先调度小的。
- 如果都大于自身的最小分享量,则计算当前运行任务数量占自身weight的比值。优先调度小的。
- 其他情况,根据调度对象的名称判断
private[spark] class FairSchedulingAlgorithm extends SchedulingAlgorithm {
override def comparator(s1: Schedulable, s2: Schedulable): Boolean = {
val minShare1 = s1.minShare
val minShare2 = s2.minShare
val runningTasks1 = s1.runningTasks
val runningTasks2 = s2.runningTasks
val s1Needy = runningTasks1 < minShare1
val s2Needy = runningTasks2 < minShare2
val minShareRatio1 = runningTasks1.toDouble / math.max(minShare1, 1.0)
val minShareRatio2 = runningTasks2.toDouble / math.max(minShare2, 1.0)
val taskToWeightRatio1 = runningTasks1.toDouble / s1.weight.toDouble
val taskToWeightRatio2 = runningTasks2.toDouble / s2.weight.toDouble
var compare = 0
if (s1Needy && !s2Needy) {
return true
} else if (!s1Needy && s2Needy) {
return false
} else if (s1Needy && s2Needy) {
compare = minShareRatio1.compareTo(minShareRatio2)
} else {
compare = taskToWeightRatio1.compareTo(taskToWeightRatio2)
}
if (compare < 0) {
true
} else if (compare > 0) {
false
} else {
s1.name < s2.name
}
}
}
调度池构建器
特质SchedulableBuilder定义了调度池构建器的行为规范
rootPool: 返回根调度池buildPools: 对调度池进行构建addTaskSetManager: 向调度池内添加TaskSetManager
有以下两个子类
FIFOSchedulableBuilder
用于创建先进先出的调度池。由代码可知,该调度池构建器产生的调度池只有一层调度队列,根调度池中都是TaskSetManager
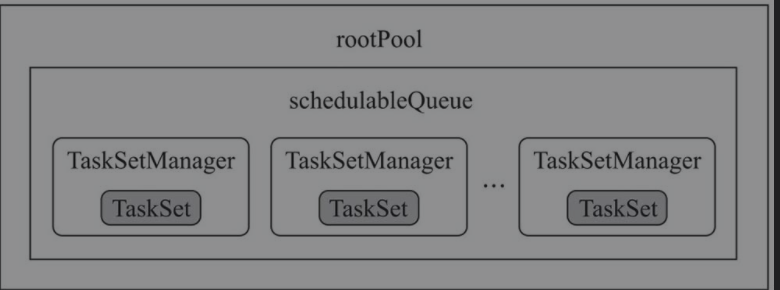
private[spark] class FIFOSchedulableBuilder(val rootPool: Pool)
extends SchedulableBuilder with Logging {
override def buildPools() {
// nothing
}
override def addTaskSetManager(manager: Schedulable, properties: Properties) {
rootPool.addSchedulable(manager)
}
}
FairSchedulableBuilder
用于创建公平调度池。
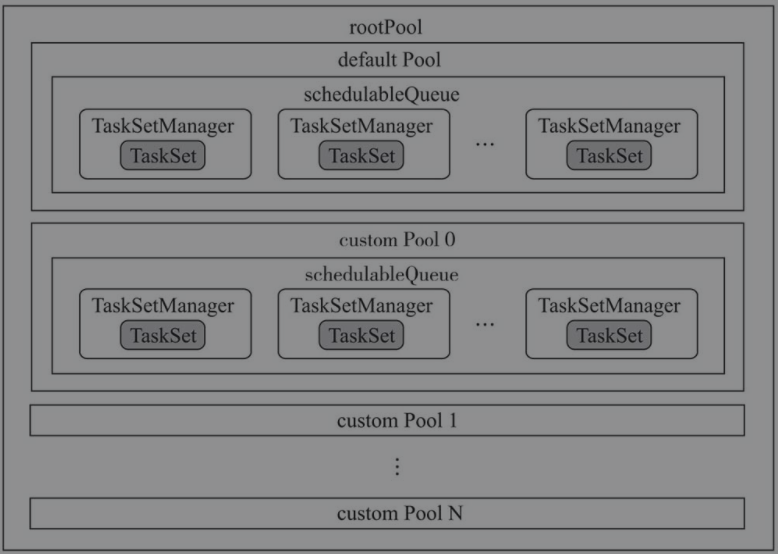
下面是重要的成员属性
schedulerAllocFile: 调度分配文件,由spark.scheduler.allocation.file配置DEFAULT_SCHEDULER_FILE: 默认调度分配文件fairscheduler.xml。每个调度池需要指定weight和minShare,且每个调度池内可以选择不同的调度算法<allocations> <pool name="production"> <schedulingMode>FAIR</schedulingMode> <weight>1</weight> <minShare>2</minShare> </pool> <pool name="test"> <schedulingMode>FIFO</schedulingMode> <weight>2</weight> <minShare>3</minShare> </pool> </allocations>
有以下常量成员属性
val DEFAULT_POOL_NAME = "default"
val MINIMUM_SHARES_PROPERTY = "minShare"
val SCHEDULING_MODE_PROPERTY = "schedulingMode"
val WEIGHT_PROPERTY = "weight"
val POOL_NAME_PROPERTY = "@name"
val POOLS_PROPERTY = "pool"
val DEFAULT_SCHEDULING_MODE = SchedulingMode.FIFO
val DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SHARE = 0
val DEFAULT_WEIGHT = 1
下面是重要的成员方法
buildPools(): 读取调度分配文件并调用buildFairSchedulerPool()构建公平调度池,最后调用buildDefaultPool()构建默认的调度池buildFairSchedulerPool(): 往rootPool(公平调度池)中添加配置文件中的调度池buildDefaultPool(): 如果调度池中没有名为default调度池,则在rootPool(公平调度池)中添加一个完全默认的调度池addTaskSetManager(): 将一个TaskSetManager添加到调度池中- 如果没有指定调度池名称,则默认将
TaskSetManager加到default池中 - 如果没有找到该调度池,则构建一个默认属性的该名称的调度池加入
rootPool中,将TaskSetManager加到该调度池中
override def addTaskSetManager(manager: Schedulable, properties: Properties) { val poolName = if (properties != null) { properties.getProperty(FAIR_SCHEDULER_PROPERTIES, DEFAULT_POOL_NAME) } else { DEFAULT_POOL_NAME } var parentPool = rootPool.getSchedulableByName(poolName) if (parentPool == null) { // we will create a new pool that user has configured in app // instead of being defined in xml file parentPool = new Pool(poolName, DEFAULT_SCHEDULING_MODE, DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SHARE, DEFAULT_WEIGHT) rootPool.addSchedulable(parentPool) logWarning(s"A job was submitted with scheduler pool $poolName, which has not been " + "configured. This can happen when the file that pools are read from isn't set, or " + s"when that file doesn't contain $poolName. Created $poolName with default " + s"configuration (schedulingMode: $DEFAULT_SCHEDULING_MODE, " + s"minShare: $DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SHARE, weight: $DEFAULT_WEIGHT)") } parentPool.addSchedulable(manager) logInfo("Added task set " + manager.name + " tasks to pool " + poolName) }- 如果没有指定调度池名称,则默认将
调度池
如图所示,调度池是一个多层次的调度队列。
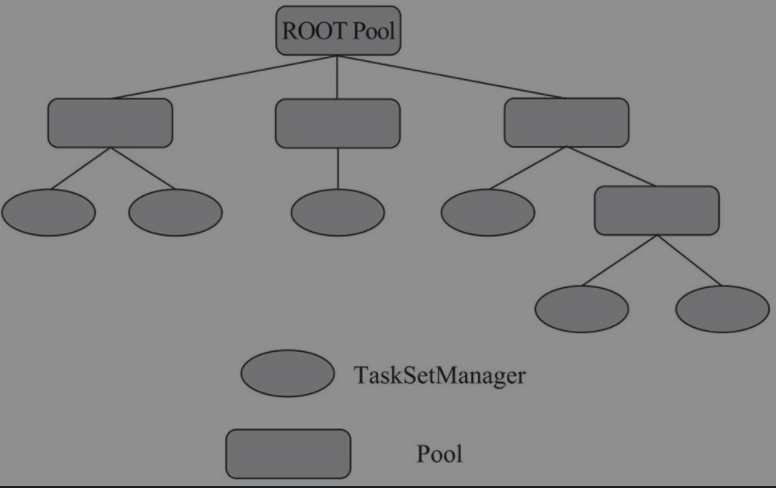
Pool
调度池Pool实现了Schedulable,包含以下成员属性
parent: 当前Pool的父PoolschedulingMode: 枚举类型,FAIR、FIFO、NONEschedulableQueue:ConcurrentLinkedQueue[Schedulable],用于存储SchedulableschedulableNameToSchedulable:ConcurrentHashMap[String, Schedulable]。调度名称与Schedulable的对应关系runningTasks: 当前正在运行的任务数量priority: 进行调度的优先级stageId: 所属Stage的身份标识name,poolName: 调度池名称taskSetSchedulingAlgorithm: 调度算法,与schedulingMode一致,默认为FIFOSchedulingAlgorithm
以下是重要的成员方法
addSchedulable(),removeSchedulable(): 从schedulableQueue和schedulableNameToSchedulable中增加或删除SchedulablegetSchedulableByName(): 先从当前调度队列中查找,如果没找到就从子调度队列中查找override def getSchedulableByName(schedulableName: String): Schedulable = { if (schedulableNameToSchedulable.containsKey(schedulableName)) { return schedulableNameToSchedulable.get(schedulableName) } for (schedulable <- schedulableQueue.asScala) { val sched = schedulable.getSchedulableByName(schedulableName) if (sched != null) { return sched } } null }executorLost(): 传递executor给所有的子Schedulable,所有此executor上的task会重新提交执行checkSpeculatableTasks(): 检查是否有需要推测执行的taskgetSortedTaskSetQueue(): 返回按照调度算法排序后的调度队列increaseRunningTasks(): 增加当前Pool及其父Pool中记录的当前正在运行的任务数量decreaseRunningTasks(): 减少当前Pool及其父Pool中记录的当前正在运行的任务数量
TaskSetManager
TaskSetManager实现了Schedulable特质,并参与到调度池的调度中,对TaskSet进行管理,包括任务推断、Task本地性,并对Task进行资源分配。
下面是TaskSet的定义
private[spark] class TaskSet(
val tasks: Array[Task[_]],
val stageId: Int,
val stageAttemptId: Int,
val priority: Int,
val properties: Properties) {
val id: String = stageId + "." + stageAttemptId
override def toString: String = "TaskSet " + id
}
TaskSetManager包含以下重要的成员属性
sched:TaskSetManager所属的TaskSchedulerImpltaskSet: 当前TaskSetManager管理的TaskSetmaxTaskFailures: 最大任务失败次数SPECULATION_QUANTILE: 推测执行的任务分数。通过spark.speculation.quantile进行配置,默认为0.75SPECULATION_MULTIPLIER: 推测执行的任务乘数。通过spark.speculation.multiplier属性进行配置,默认为1.5maxResultSize: action算子结果的大小限制,防止Driver出现OOM。通过spark.driver.maxResultSize属性进行配置,默认为1GBtasks: TaskSet.tasksnumTasks: tasks数组的长度copiesRunning: 每个Task的复制执行的计数数组。与tasks的索引位置一致successful: 每个Task是否执行成功的标记数组。与tasks的索引位置一致numFailures: 每个Task执行失败的计数数组。与tasks的索引位置一致taskAttempts:Array[List[TaskInfo]]。对每个Task的所有执行尝试信息(TaskInfo)的记录数组。与tasks的索引位置一致tasksSuccessful: 执行成功的Task数量parent:TaskSetManager的父PooltotalResultSize: 所有Task执行结果的总大小calculatedTasks: 计算过的Task数量taskSetBlacklistHelperOpt: TaskSetManager所管理的TaskSet的Executor黑名单runningTasksSet:HashSet[Long]。正在运行的Task的集合。runningTasks: 正在运行的Task的数量。runningTasksSet.sizeisZombie: 当TaskSetManager所管理的TaskSet中的所有task都执行成功了,不再有更多的task尝试被启动时,就处于僵尸状态pendingTasksForExecutor: 每个Executor上待处理的task的集合pendingTasksForHost: 每个Host上待处理的task的集合pendingTasksForRack: 每个机架上待处理的task的集合pendingTasksWithNoPrefs: 没有任何本地性偏好的待处理task集合allPendingTasks: 所有待处理的task集合speculatableTasks: 能够进行推测执行的task集合taskInfos:HashMap[Long, TaskInfo]。task与task尝试信息的映射关系myLocalityLevels: 当前TaskSetManager内允许的task本地性级别数组。由computeValidLocalityLevels()方法初始化- 有五种本地性,描述了数据和运行代码的距离,分配优先级由高到低分别为,
PROCESS_LOCAL(本地进程),NODE_LOCAL(本地节点),NO_PREF(没有偏好),RACK_LOCAL(本地机架),ANY(任何,不在一个机架上) - 如果存在Executor上待处理的task并且其中存在激活的Executor,则允许本地性级别中包含
PROCESS_LOCAL - 如果存在Host上待处理的Task的集合并且其中存在激活的Executor,则允许本地性级别中包含
NODE_LOCAL - 如果存在没有任何本地性偏好的待处理Task,则允许本地性级别中包含
NO_PREF - 如果存在机架上待处理的Task的集合并且其中存在激活的Host,则允许本地性级别中包含
RACK_LOCAL - 允许本地性级别中包含
ANY
private def computeValidLocalityLevels(): Array[TaskLocality.TaskLocality] = { import TaskLocality.{PROCESS_LOCAL, NODE_LOCAL, NO_PREF, RACK_LOCAL, ANY} val levels = new ArrayBuffer[TaskLocality.TaskLocality] if (!pendingTasksForExecutor.isEmpty && pendingTasksForExecutor.keySet.exists(sched.isExecutorAlive(_))) { levels += PROCESS_LOCAL } if (!pendingTasksForHost.isEmpty && pendingTasksForHost.keySet.exists(sched.hasExecutorsAliveOnHost(_))) { levels += NODE_LOCAL } if (!pendingTasksWithNoPrefs.isEmpty) { levels += NO_PREF } if (!pendingTasksForRack.isEmpty && pendingTasksForRack.keySet.exists(sched.hasHostAliveOnRack(_))) { levels += RACK_LOCAL } levels += ANY logDebug("Valid locality levels for " + taskSet + ": " + levels.mkString(", ")) levels.toArray }- 有五种本地性,描述了数据和运行代码的距离,分配优先级由高到低分别为,
localityWaits: 与myLocalityLevels中的每个本地性级别相对应的等待时间,用于延迟调度- 默认等待时间通过
spark.locality.wait属性配置,默认为3秒 - 根据本地性获取对应属性中的等待时间
private def getLocalityWait(level: TaskLocality.TaskLocality): Long = { val defaultWait = conf.get(config.LOCALITY_WAIT) val localityWaitKey = level match { case TaskLocality.PROCESS_LOCAL => "spark.locality.wait.process" case TaskLocality.NODE_LOCAL => "spark.locality.wait.node" case TaskLocality.RACK_LOCAL => "spark.locality.wait.rack" case _ => null } if (localityWaitKey != null) { conf.getTimeAsMs(localityWaitKey, defaultWait.toString) } else { 0L } }- 默认等待时间通过
currentLocalityIndex: 当前的本地性级别在myLocalityLevels中的索引lastLaunchTime: 在当前的本地性级别上运行Task的时间successfulTaskDurations:MedianHeap类型,维护两个优先队列用于快速获取可能重复的一组数字的中位数,LeetCode上有类似的题目- 两个优先队列。
smallerHalf是大根堆,堆顶元素为当前的中位数。largerHalf是小根堆,堆顶元素是当前中位数 - 如
insert()方法所示,如果插入数大于median()计算出来的中位数则插入largerHalf,否则插入smallerHalf。如果整个队列为空则插入largerHalf。可知时间复杂度为O(logn) - 如
rebalance()方法所示,每次插入完都要再平衡,取出大的堆中的元素放入另一个堆中,使得两个堆的大小相差不超过1 - 如
median()方法所示,如果两个堆大小相同(总数为偶数),则返回两个堆顶元素的平均值,否则(总数为奇数)返回更大的那个堆的堆顶元素。可知时间复杂度为O(logn)
private[spark] class MedianHeap(implicit val ord: Ordering[Double]) { /** * Stores all the numbers less than the current median in a smallerHalf, * i.e median is the maximum, at the root. */ private[this] var smallerHalf = PriorityQueue.empty[Double](ord) /** * Stores all the numbers greater than the current median in a largerHalf, * i.e median is the minimum, at the root. */ private[this] var largerHalf = PriorityQueue.empty[Double](ord.reverse) def isEmpty(): Boolean = { smallerHalf.isEmpty && largerHalf.isEmpty } def size(): Int = { smallerHalf.size + largerHalf.size } def insert(x: Double): Unit = { // If both heaps are empty, we arbitrarily insert it into a heap, let's say, the largerHalf. if (isEmpty) { largerHalf.enqueue(x) } else { // If the number is larger than current median, it should be inserted into largerHalf, // otherwise smallerHalf. if (x > median) { largerHalf.enqueue(x) } else { smallerHalf.enqueue(x) } } rebalance() } private[this] def rebalance(): Unit = { if (largerHalf.size - smallerHalf.size > 1) { smallerHalf.enqueue(largerHalf.dequeue()) } if (smallerHalf.size - largerHalf.size > 1) { largerHalf.enqueue(smallerHalf.dequeue) } } def median: Double = { if (isEmpty) { throw new NoSuchElementException("MedianHeap is empty.") } if (largerHalf.size == smallerHalf.size) { (largerHalf.head + smallerHalf.head) / 2.0 } else if (largerHalf.size > smallerHalf.size) { largerHalf.head } else { smallerHalf.head } } }- 两个优先队列。
下面介绍与本地性相关的成员方法
getLocalityIndex(): 从myLocalityLevels中找出指定的本地性级别所对应的索引。返回低于给定本地性级别中级别最高的索引def getLocalityIndex(locality: TaskLocality.TaskLocality): Int = { var index = 0 while (locality > myLocalityLevels(index)) { index += 1 } index }getAllowedLocalityLevel(): 获取允许的本地性级别,延迟调度的核心方法tasksNeedToBeScheduledFrom()判断list是否有task需要调度,同时此方法还会在找到需要调度的task前将访问到的已经完成或者调度的task从pendingTaskIds中移除moreTasksToRunIn()与tasksNeedToBeScheduledFrom()作用一样,同时惰性删除pendingTasks中的Executor- 从
currentLocalityIndex开始从myLocalityLevels中不断向后,不断循环降级 - 判断是否有待调度的当前级别的task
- 如果没有则降低本地性级别进入下一个循环
- 如果有则判断与上一个task的最后运行时间是否大于对应当前级别的等待时间,如果大于则将最后运行时间累加当前级别等待时间并进入下一个循环(之后的循环中如果一旦存在等待task则立即返回该等级),如果小于则返回当前级别
- 当循环结束时,返回的就是
ANY级别
private def getAllowedLocalityLevel(curTime: Long): TaskLocality.TaskLocality = { // Remove the scheduled or finished tasks lazily def tasksNeedToBeScheduledFrom(pendingTaskIds: ArrayBuffer[Int]): Boolean = { var indexOffset = pendingTaskIds.size while (indexOffset > 0) { indexOffset -= 1 val index = pendingTaskIds(indexOffset) if (copiesRunning(index) == 0 && !successful(index)) { return true } else { pendingTaskIds.remove(indexOffset) } } false } // Walk through the list of tasks that can be scheduled at each location and returns true // if there are any tasks that still need to be scheduled. Lazily cleans up tasks that have // already been scheduled. def moreTasksToRunIn(pendingTasks: HashMap[String, ArrayBuffer[Int]]): Boolean = { val emptyKeys = new ArrayBuffer[String] val hasTasks = pendingTasks.exists { case (id: String, tasks: ArrayBuffer[Int]) => if (tasksNeedToBeScheduledFrom(tasks)) { true } else { emptyKeys += id false } } // The key could be executorId, host or rackId emptyKeys.foreach(id => pendingTasks.remove(id)) hasTasks } while (currentLocalityIndex < myLocalityLevels.length - 1) { val moreTasks = myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex) match { case TaskLocality.PROCESS_LOCAL => moreTasksToRunIn(pendingTasksForExecutor) case TaskLocality.NODE_LOCAL => moreTasksToRunIn(pendingTasksForHost) case TaskLocality.NO_PREF => pendingTasksWithNoPrefs.nonEmpty case TaskLocality.RACK_LOCAL => moreTasksToRunIn(pendingTasksForRack) } if (!moreTasks) { // This is a performance optimization: if there are no more tasks that can // be scheduled at a particular locality level, there is no point in waiting // for the locality wait timeout (SPARK-4939). lastLaunchTime = curTime logDebug(s"No tasks for locality level ${myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex)}, " + s"so moving to locality level ${myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex + 1)}") currentLocalityIndex += 1 } else if (curTime - lastLaunchTime >= localityWaits(currentLocalityIndex)) { // Jump to the next locality level, and reset lastLaunchTime so that the next locality // wait timer doesn't immediately expire lastLaunchTime += localityWaits(currentLocalityIndex) logDebug(s"Moving to ${myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex + 1)} after waiting for " + s"${localityWaits(currentLocalityIndex)}ms") currentLocalityIndex += 1 } else { return myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex) } } myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex) }
下面介绍与推测执行有关的成员方法
checkSpeculatableTasks(): 检查当前TaskSetManager中是否有需要推测执行的task,由TaskSchedulerImpl中的推测线程池调用,固定时间间隔进行检查- 处于僵尸状态或者使用屏障调度器或者只有一个task,将不会开启推测执行
- 计算推测执行的最小完成task数量,值为
SPECULATION_QUANTILE与总任务数的乘积向下取整 - 如果已经完成的task数量比最小完成task数量大,则继续判断,否则返回false
- 由
successfulTaskDurations获得当前已完成task执行时间的中位数,计算最小推测时间,其值为SPECULATION_MULTIPLIER和中位数的乘积,取结果和minTimeToSpeculation的最大值 - 遍历正在运行的task,找出符合最小推测时间,未执行成功,复制运行数为1,不是推测执行的task,并在此
TaskSetManager中注册,调用DagScheduler.speculativeTaskSubmitted()通知提交了推测执行task - 如果找到了可以推测执行的task则返回true
override def checkSpeculatableTasks(minTimeToSpeculation: Int): Boolean = { // Can't speculate if we only have one task, and no need to speculate if the task set is a // zombie or is from a barrier stage. if (isZombie || isBarrier || numTasks == 1) { return false } var foundTasks = false val minFinishedForSpeculation = (SPECULATION_QUANTILE * numTasks).floor.toInt logDebug("Checking for speculative tasks: minFinished = " + minFinishedForSpeculation) if (tasksSuccessful >= minFinishedForSpeculation && tasksSuccessful > 0) { val time = clock.getTimeMillis() val medianDuration = successfulTaskDurations.median val threshold = max(SPECULATION_MULTIPLIER * medianDuration, minTimeToSpeculation) // TODO: Threshold should also look at standard deviation of task durations and have a lower // bound based on that. logDebug("Task length threshold for speculation: " + threshold) for (tid <- runningTasksSet) { val info = taskInfos(tid) val index = info.index if (!successful(index) && copiesRunning(index) == 1 && info.timeRunning(time) > threshold && !speculatableTasks.contains(index)) { logInfo( "Marking task %d in stage %s (on %s) as speculatable because it ran more than %.0f ms" .format(index, taskSet.id, info.host, threshold)) speculatableTasks += index sched.dagScheduler.speculativeTaskSubmitted(tasks(index)) foundTasks = true } } } foundTasks }dequeueSpeculativeTask: 根据指定的Host、Executor和本地性级别,从推测Task中根据指定的参数找出task和相应的本地性级别,一次只会返回一个task- 从
speculatableTasks中移除已经完成的推测task - 遍历未在Host上执行且Host和Executor都未在黑名单上的推测task。且指定的Executor在该推测task的偏好位置中,则从
speculatableTasks中移除该task并返回task id和PROCESS_LOCAL二元组,表示从推测队列中取出这个符合条件的推测task - 如果循环中没有返回任何值,则进一步判断。如果指定的本地性等级小于等于NODE_LOCAL,则与上一个循环一样,并且找到指定Host在task的偏好位置的task,从推测队列中取出并返回
- 接下来的判断与上两个循环一致,分别判断NO_PREF和RACK_LOCAL等级
- 如果都没有返回值,那么就返回(task id, ANY)
- 由此可以看出指定的本地性等级参数为最低本地性要求,此方法会优先返回高本地性的推测task
protected def dequeueSpeculativeTask(execId: String, host: String, locality: TaskLocality.Value) : Option[(Int, TaskLocality.Value)] = { speculatableTasks.retain(index => !successful(index)) // Remove finished tasks from set def canRunOnHost(index: Int): Boolean = { !hasAttemptOnHost(index, host) && !isTaskBlacklistedOnExecOrNode(index, execId, host) } if (!speculatableTasks.isEmpty) { // Check for process-local tasks; note that tasks can be process-local // on multiple nodes when we replicate cached blocks, as in Spark Streaming for (index <- speculatableTasks if canRunOnHost(index)) { val prefs = tasks(index).preferredLocations val executors = prefs.flatMap(_ match { case e: ExecutorCacheTaskLocation => Some(e.executorId) case _ => None }); if (executors.contains(execId)) { speculatableTasks -= index return Some((index, TaskLocality.PROCESS_LOCAL)) } } // Check for node-local tasks if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(locality, TaskLocality.NODE_LOCAL)) { for (index <- speculatableTasks if canRunOnHost(index)) { val locations = tasks(index).preferredLocations.map(_.host) if (locations.contains(host)) { speculatableTasks -= index return Some((index, TaskLocality.NODE_LOCAL)) } } } // Check for no-preference tasks if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(locality, TaskLocality.NO_PREF)) { for (index <- speculatableTasks if canRunOnHost(index)) { val locations = tasks(index).preferredLocations if (locations.size == 0) { speculatableTasks -= index return Some((index, TaskLocality.PROCESS_LOCAL)) } } } // Check for rack-local tasks if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(locality, TaskLocality.RACK_LOCAL)) { for (rack <- sched.getRackForHost(host)) { for (index <- speculatableTasks if canRunOnHost(index)) { val racks = tasks(index).preferredLocations.map(_.host).flatMap(sched.getRackForHost) if (racks.contains(rack)) { speculatableTasks -= index return Some((index, TaskLocality.RACK_LOCAL)) } } } } // Check for non-local tasks if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(locality, TaskLocality.ANY)) { for (index <- speculatableTasks if canRunOnHost(index)) { speculatableTasks -= index return Some((index, TaskLocality.ANY)) } } } None }- 从
下面介绍一些重要的其他成员方法
addPendingTask(): 根据task的偏好位置向等待调度task列表(pendingTasksForExecutor,pendingTasksForHost,pendingTasksForRack,pendingTasksWithNoPrefs,allPendingTasks)中添加taskprivate[spark] def addPendingTask(index: Int) { for (loc <- tasks(index).preferredLocations) { loc match { case e: ExecutorCacheTaskLocation => pendingTasksForExecutor.getOrElseUpdate(e.executorId, new ArrayBuffer) += index case e: HDFSCacheTaskLocation => val exe = sched.getExecutorsAliveOnHost(loc.host) exe match { case Some(set) => for (e <- set) { pendingTasksForExecutor.getOrElseUpdate(e, new ArrayBuffer) += index } logInfo(s"Pending task $index has a cached location at ${e.host} " + ", where there are executors " + set.mkString(",")) case None => logDebug(s"Pending task $index has a cached location at ${e.host} " + ", but there are no executors alive there.") } case _ => } pendingTasksForHost.getOrElseUpdate(loc.host, new ArrayBuffer) += index for (rack <- sched.getRackForHost(loc.host)) { pendingTasksForRack.getOrElseUpdate(rack, new ArrayBuffer) += index } } if (tasks(index).preferredLocations == Nil) { pendingTasksWithNoPrefs += index } allPendingTasks += index // No point scanning this whole list to find the old task there }dequeueTaskFromList(): 在给定task列表中从后往前找到一个给定Executor和host对于该task不在黑名单中,且没有复制运行且没有执行成功的taskprivate def dequeueTaskFromList( execId: String, host: String, list: ArrayBuffer[Int]): Option[Int] = { var indexOffset = list.size while (indexOffset > 0) { indexOffset -= 1 val index = list(indexOffset) if (!isTaskBlacklistedOnExecOrNode(index, execId, host)) { // This should almost always be list.trimEnd(1) to remove tail list.remove(indexOffset) if (copiesRunning(index) == 0 && !successful(index)) { return Some(index) } } } None } private def isTaskBlacklistedOnExecOrNode(index: Int, execId: String, host: String): Boolean = { taskSetBlacklistHelperOpt.exists { blacklist => blacklist.isNodeBlacklistedForTask(host, index) || blacklist.isExecutorBlacklistedForTask(execId, index) } }dequeueTask(): 根据指定的Host和Executor和最大本地性级别从task等待队列中,找出并返回(task, 本地性级别, 是否推测执行)- 调用了
dequeueTaskFromList()在pendingTasksForExecutor中寻找,如果找到就返回(task, PROCESS_LOCAL, false) - 如果没找到则降级继续寻找,先判断是否满足最大本地性级别要求,跟之前一样调用
dequeueTaskFromList()分别在pendingTasksForHost,pendingTasksWithNoPrefs,pendingTasksForRack和allPendingTasks(本地性级别为ANY)中寻找 - 如果还没找到,则调用
dequeueSpeculativeTask()返回需要推测执行的task
private def dequeueTask(execId: String, host: String, maxLocality: TaskLocality.Value) : Option[(Int, TaskLocality.Value, Boolean)] = { // pendingTasksForExecutor for (index <- dequeueTaskFromList(execId, host, getPendingTasksForExecutor(execId))) { return Some((index, TaskLocality.PROCESS_LOCAL, false)) } if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(maxLocality, TaskLocality.NODE_LOCAL)) { // pendingTasksForHost for (index <- dequeueTaskFromList(execId, host, getPendingTasksForHost(host))) { return Some((index, TaskLocality.NODE_LOCAL, false)) } } if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(maxLocality, TaskLocality.NO_PREF)) { // Look for noPref tasks after NODE_LOCAL for minimize cross-rack traffic for (index <- dequeueTaskFromList(execId, host, pendingTasksWithNoPrefs)) { return Some((index, TaskLocality.PROCESS_LOCAL, false)) } } if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(maxLocality, TaskLocality.RACK_LOCAL)) { // pendingTasksForRack for { rack <- sched.getRackForHost(host) index <- dequeueTaskFromList(execId, host, getPendingTasksForRack(rack)) } { return Some((index, TaskLocality.RACK_LOCAL, false)) } } if (TaskLocality.isAllowed(maxLocality, TaskLocality.ANY)) { for (index <- dequeueTaskFromList(execId, host, allPendingTasks)) { return Some((index, TaskLocality.ANY, false)) } } // find a speculative task if all others tasks have been scheduled dequeueSpeculativeTask(execId, host, maxLocality).map { case (taskIndex, allowedLocality) => (taskIndex, allowedLocality, true)} }- 调用了
addRunningTask(),removeRunningTask(): 在此TaskSetManager中添加删除task,调用父调度池的increaseRunningTasks()或者decreaseRunningTasks()方法,将效果向上传播def addRunningTask(tid: Long) { if (runningTasksSet.add(tid) && parent != null) { parent.increaseRunningTasks(1) } } def removeRunningTask(tid: Long) { if (runningTasksSet.remove(tid) && parent != null) { parent.decreaseRunningTasks(1) } }maybeFinishTaskSet(): 当此TaskSet已经完成时(非僵尸状态且没有正在运行的task),向TaskSchedulerImpl注册已完成并更新黑名单private def maybeFinishTaskSet() { if (isZombie && runningTasks == 0) { sched.taskSetFinished(this) if (tasksSuccessful == numTasks) { blacklistTracker.foreach(_.updateBlacklistForSuccessfulTaskSet( taskSet.stageId, taskSet.stageAttemptId, taskSetBlacklistHelperOpt.get.execToFailures)) } } }resourceOffer(): 给定Executor和Host,最大本地性等级,给task分配资源- 当给定的Executor或Host在黑名单中,或者处于僵尸状态时,直接返回
None - 如果最大本地性不是
NO_PREF,则allowedLocality为最大本地性和延迟调度getAllowedLocalityLevel()返回的等级较高的一个 - 将
allowedLocality传入dequeueTask()方法,取出一个task - 生成attempt id,task id和
TaskInfo并记录,对应task的copiesRunning增加 - 如果最大本地性等级不是
NO_PREF则调用getLocalityIndex()更新currentLocalityIndex和lastLaunchTime以维持延迟调度,没有本地性偏好不会对延迟调度有影响 - 序列化task,当体积大于100KB时会打印警告,调用
addRunningTask()标记运行task,并调用dagScheduler.taskStarted()投递BeginEvent事件并返回TaskDescription
def resourceOffer( execId: String, host: String, maxLocality: TaskLocality.TaskLocality) : Option[TaskDescription] = { val offerBlacklisted = taskSetBlacklistHelperOpt.exists { blacklist => blacklist.isNodeBlacklistedForTaskSet(host) || blacklist.isExecutorBlacklistedForTaskSet(execId) } if (!isZombie && !offerBlacklisted) { val curTime = clock.getTimeMillis() var allowedLocality = maxLocality if (maxLocality != TaskLocality.NO_PREF) { allowedLocality = getAllowedLocalityLevel(curTime) if (allowedLocality > maxLocality) { // We're not allowed to search for farther-away tasks allowedLocality = maxLocality } } dequeueTask(execId, host, allowedLocality).map { case ((index, taskLocality, speculative)) => // Found a task; do some bookkeeping and return a task description val task = tasks(index) val taskId = sched.newTaskId() // Do various bookkeeping copiesRunning(index) += 1 val attemptNum = taskAttempts(index).size val info = new TaskInfo(taskId, index, attemptNum, curTime, execId, host, taskLocality, speculative) taskInfos(taskId) = info taskAttempts(index) = info :: taskAttempts(index) // Update our locality level for delay scheduling // NO_PREF will not affect the variables related to delay scheduling if (maxLocality != TaskLocality.NO_PREF) { currentLocalityIndex = getLocalityIndex(taskLocality) lastLaunchTime = curTime } // Serialize and return the task val serializedTask: ByteBuffer = try { ser.serialize(task) } catch { // If the task cannot be serialized, then there's no point to re-attempt the task, // as it will always fail. So just abort the whole task-set. case NonFatal(e) => val msg = s"Failed to serialize task $taskId, not attempting to retry it." logError(msg, e) abort(s"$msg Exception during serialization: $e") throw new TaskNotSerializableException(e) } if (serializedTask.limit() > TaskSetManager.TASK_SIZE_TO_WARN_KB * 1024 && !emittedTaskSizeWarning) { emittedTaskSizeWarning = true logWarning(s"Stage ${task.stageId} contains a task of very large size " + s"(${serializedTask.limit() / 1024} KB). The maximum recommended task size is " + s"${TaskSetManager.TASK_SIZE_TO_WARN_KB} KB.") } addRunningTask(taskId) // We used to log the time it takes to serialize the task, but task size is already // a good proxy to task serialization time. // val timeTaken = clock.getTime() - startTime val taskName = s"task ${info.id} in stage ${taskSet.id}" logInfo(s"Starting $taskName (TID $taskId, $host, executor ${info.executorId}, " + s"partition ${task.partitionId}, $taskLocality, ${serializedTask.limit()} bytes)") sched.dagScheduler.taskStarted(task, info) new TaskDescription( taskId, attemptNum, execId, taskName, index, task.partitionId, addedFiles, addedJars, task.localProperties, serializedTask) } } else { None } }- 当给定的Executor或Host在黑名单中,或者处于僵尸状态时,直接返回
executorLost(): 处理Executor不可用的情况- 如果此
TaskSetManager管理的TaskSet中的task为ShuffleMapTask,并且应用没有提供外部的Shuffle服务,并不处于僵尸状态则将taskInfos中的所有在指定Executor上执行成功的Task重置成功状态并加入到等待task中,并调用DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop.taskEnded()发送CompletionEvent事件,此CompletionEvent将携带Resubmitted,避免CompletionEvent的关心者在Stage的所有Task都完成后认为当前的Stage也执行完成,而是让它们知道此Task将被重新提交 - 遍历正在此Executor上正在运行的task,调用
handleFailedTask()并传入Executor的不可用原因
override def executorLost(execId: String, host: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason) { // Re-enqueue any tasks that ran on the failed executor if this is a shuffle map stage, // and we are not using an external shuffle server which could serve the shuffle outputs. // The reason is the next stage wouldn't be able to fetch the data from this dead executor // so we would need to rerun these tasks on other executors. if (tasks(0).isInstanceOf[ShuffleMapTask] && !env.blockManager.externalShuffleServiceEnabled && !isZombie) { for ((tid, info) <- taskInfos if info.executorId == execId) { val index = taskInfos(tid).index // We may have a running task whose partition has been marked as successful, // this partition has another task completed in another stage attempt. // We treat it as a running task and will call handleFailedTask later. if (successful(index) && !info.running && !killedByOtherAttempt.contains(tid)) { successful(index) = false copiesRunning(index) -= 1 tasksSuccessful -= 1 addPendingTask(index) // Tell the DAGScheduler that this task was resubmitted so that it doesn't think our // stage finishes when a total of tasks.size tasks finish. sched.dagScheduler.taskEnded( tasks(index), Resubmitted, null, Seq.empty, info) } } } for ((tid, info) <- taskInfos if info.running && info.executorId == execId) { val exitCausedByApp: Boolean = reason match { case exited: ExecutorExited => exited.exitCausedByApp case ExecutorKilled => false case _ => true } handleFailedTask(tid, TaskState.FAILED, ExecutorLostFailure(info.executorId, exitCausedByApp, Some(reason.toString))) } // recalculate valid locality levels and waits when executor is lost recomputeLocality() }- 如果此
handleSuccessfulTask(): 标记task为执行成功并通知DAGScheduler这个task已经结束- 标记这个task已经完成,记录运行时长
- 调用
SchedulerBackend杀死关于此task的其他尝试 - 如果该
TaskSetManager的所有task已经完成了,则进入僵尸状态 - 调用
DAGScheduler.taskEnded()方法对执行结果进行处理
def handleSuccessfulTask(tid: Long, result: DirectTaskResult[_]): Unit = { val info = taskInfos(tid) val index = info.index // Check if any other attempt succeeded before this and this attempt has not been handled if (successful(index) && killedByOtherAttempt.contains(tid)) { // Undo the effect on calculatedTasks and totalResultSize made earlier when // checking if can fetch more results calculatedTasks -= 1 val resultSizeAcc = result.accumUpdates.find(a => a.name == Some(InternalAccumulator.RESULT_SIZE)) if (resultSizeAcc.isDefined) { totalResultSize -= resultSizeAcc.get.asInstanceOf[LongAccumulator].value } // Handle this task as a killed task handleFailedTask(tid, TaskState.KILLED, TaskKilled("Finish but did not commit due to another attempt succeeded")) return } info.markFinished(TaskState.FINISHED, clock.getTimeMillis()) if (speculationEnabled) { successfulTaskDurations.insert(info.duration) } removeRunningTask(tid) // Kill any other attempts for the same task (since those are unnecessary now that one // attempt completed successfully). for (attemptInfo <- taskAttempts(index) if attemptInfo.running) { logInfo(s"Killing attempt ${attemptInfo.attemptNumber} for task ${attemptInfo.id} " + s"in stage ${taskSet.id} (TID ${attemptInfo.taskId}) on ${attemptInfo.host} " + s"as the attempt ${info.attemptNumber} succeeded on ${info.host}") killedByOtherAttempt += attemptInfo.taskId sched.backend.killTask( attemptInfo.taskId, attemptInfo.executorId, interruptThread = true, reason = "another attempt succeeded") } if (!successful(index)) { tasksSuccessful += 1 logInfo(s"Finished task ${info.id} in stage ${taskSet.id} (TID ${info.taskId}) in" + s" ${info.duration} ms on ${info.host} (executor ${info.executorId})" + s" ($tasksSuccessful/$numTasks)") // Mark successful and stop if all the tasks have succeeded. successful(index) = true if (tasksSuccessful == numTasks) { isZombie = true } } else { logInfo("Ignoring task-finished event for " + info.id + " in stage " + taskSet.id + " because task " + index + " has already completed successfully") } // There may be multiple tasksets for this stage -- we let all of them know that the partition // was completed. This may result in some of the tasksets getting completed. sched.markPartitionCompletedInAllTaskSets(stageId, tasks(index).partitionId, info) sched.dagScheduler.taskEnded(tasks(index), Success, result.value(), result.accumUpdates, info) maybeFinishTaskSet() }
总结
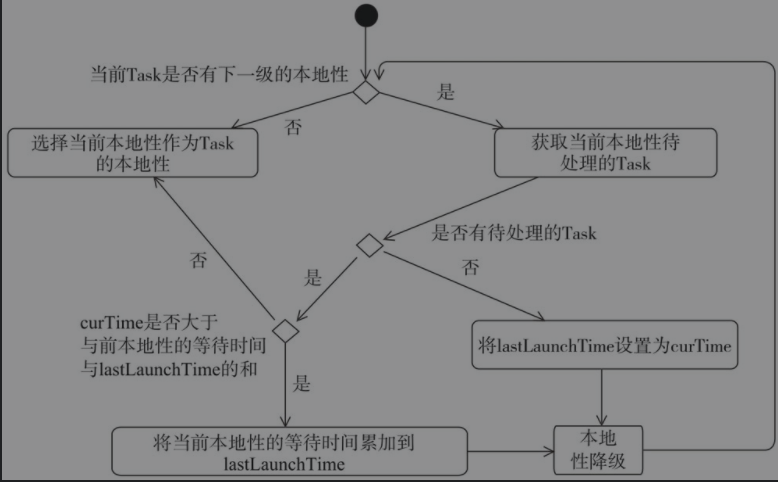
如下图所示,是延迟调度的判断过程。Spark中的延迟调度主要通过getAllowedLocalityLevel()方法实现,流程如下,优先使用上一次执行task的本地性等级,如果没有该等级的等待task或者距离上一次执行已经超过了预定时间则降级,直到找到合适的本地性等级。这样可以做到优先使用等级高的本地性等级同时避免task一直在等待这种高优先级。当资源不满足数据局部性时,暂时放弃公平性,等待后续分配,在等待一定时间后仍等不到满足局部性的资源时,则接受当前资源执行任务
REFERENCE
- Spark内核设计的艺术:架构设计与实现
文档信息
- 本文作者:wzx
- 本文链接:https://wzx140.github.io//2020/09/15/schedule-pool/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)